1. Overview
Bridge bearings play a crucial role in the safe and efficient functioning of a bridge. They transfer dead and live loads from the superstructure to the substructure (piers or abutments) while allowing controlled movements and rotations. This ensures that the bridge structure performs as designed under real working conditions.
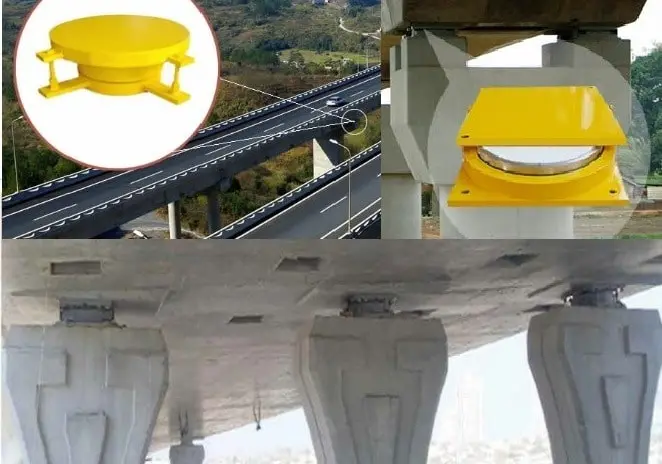

To maintain structural safety and durability, regular inspection, cleaning, and maintenance of bridge bearings are essential. Proper care prevents failures such as cracking, corrosion, aging, or displacement, which can compromise bridge performance.
2. Routine Maintenance and Inspection
Bridge bearings should be inspected and maintained at least once a year to ensure proper function and safety. Maintenance personnel should follow the guidelines below:
2.1 Visual Inspection
Each part of the bearing should be examined annually using the naked eye or a magnifying glass. Look for:
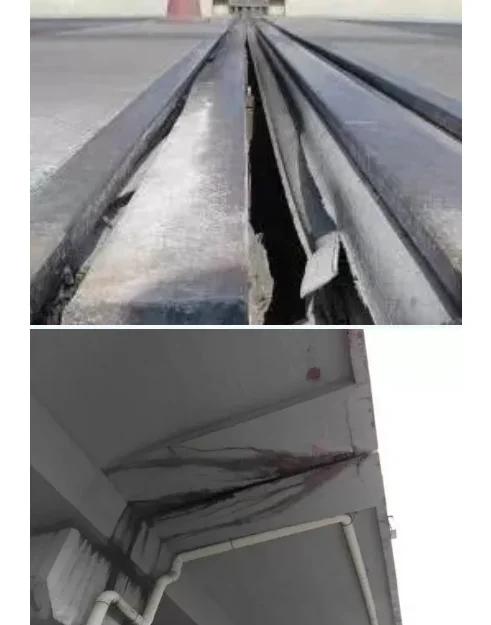
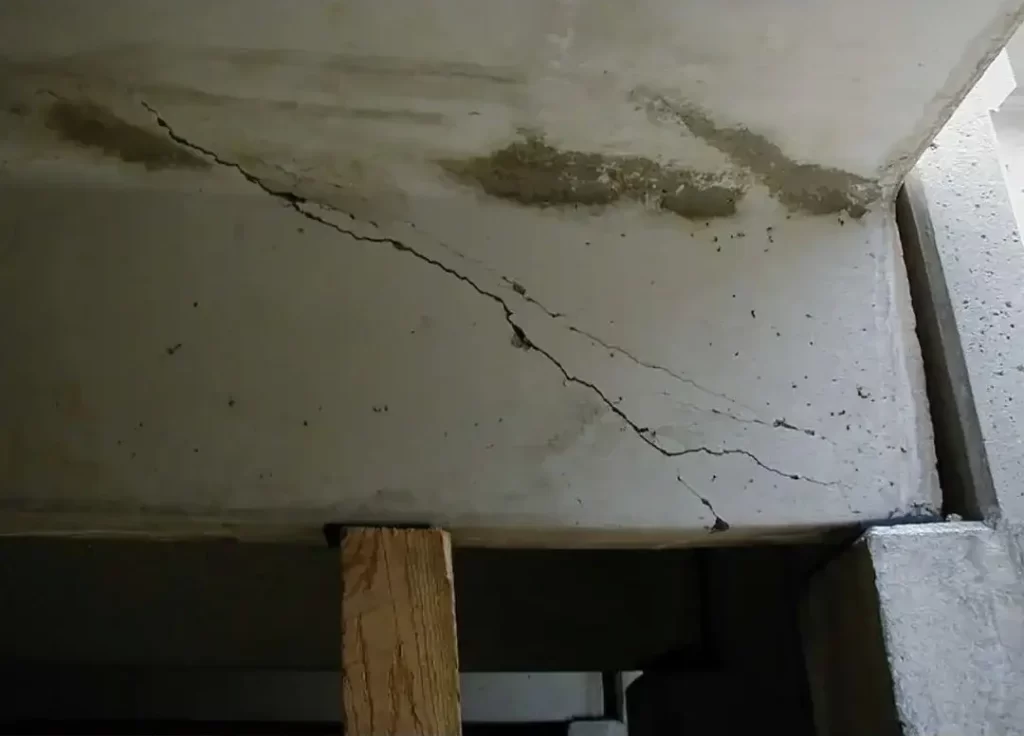
- Surface cracks or bulging
- Rubber aging and hardening
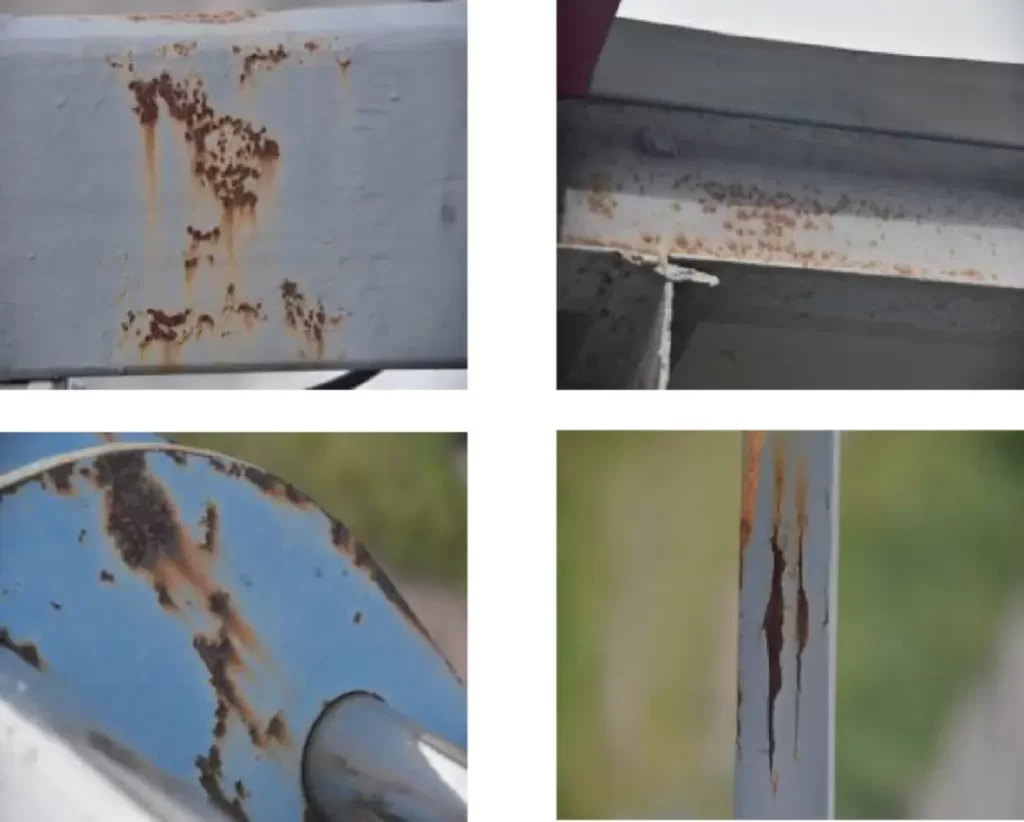
- Rust or corrosion on steel plates
- Uneven settlement or deformation
2.2 Cleanliness and Condition
Bearings must remain clean, intact, and free of debris.
- Remove dust, sand, garbage, and in winter, clear snow and ice to avoid blockage.
- Keep the bearing seat level and tight so the bridge deck can expand and contract freely.
2.3 Fixed Bearings
- Inspect and tighten anchor bolts annually.
- Ensure the bearing pad is level and in full contact with the base plate.
- Tighten any loosened connecting bolts promptly.
2.4 Metal Component Protection
- Metal surfaces must be kept rust-free.
- Apply anti-corrosion paint regularly, typically once per year.
2.5 Rubber Bearing Maintenance
Rubber bearings should remain within the designed shear deformation range. Maintenance requirements include:
- No cracks, bulging, or aging of rubber layers.
- No water accumulation or surface damage on the bearing pad.
- Replace any bearing showing excessive deformation, cracking, or crushing.
- Avoid oil or grease contact during cleaning to prevent rubber deterioration.
2.6 Bolts and Nuts
Check and tighten all fixed bolts to prevent shear damage or loosening during bridge vibration or temperature changes.
2.7 Spherical Bearings
Spherical bearings require more specialized maintenance:
- Remove dust and replace lubrication oil once per year.
- Ensure base bolts are tight and rubber seals are free of cracks or aging.
- Bearing displacement should be uniform; height difference should not exceed 3 mm.
- Repaint all steel components annually to prevent corrosion.
3. Bridge Bearing Replacement Procedures
In small and medium-span bridges, where live loads make up a large proportion of the total load, bearings are more prone to damage over time. Common issues include uneven bearing surfaces, poor load transfer, or aged and ineffective materials. When such defects occur, bearings must be adjusted or replaced promptly.
3.1 Replacement Preparation
- Use hydraulic jacks to lift the bridge superstructure slightly.
- Adjust or remove the damaged bearing carefully to avoid additional stress on the structure.
3.2 Replacement Steps
- For continuous beam bridges, end bearings can be replaced by jacking up one beam end.
- When replacing central bearings, jack up adjacent bearings simultaneously to maintain balance.
3.3 Replacement Requirements
- Rubber bearings with damage or failure must be replaced immediately.
- Bearings with uneven compression or voids should be adjusted to restore uniform contact.
- Base plates that have warped, deformed, or cracked should be repaired or replaced.
- For cases requiring elevation correction, insert steel plates or pour reinforced concrete shims based on the required height adjustment.
4. Maintenance Safety Precautions
- Always monitor bridge deformation during jacking to avoid overstressing the superstructure.
- Maintain continuous communication between field teams during bearing replacement.
- Use synchronized jacking systems to prevent torsion or uneven lifting.
- Verify all anchor bolts, bearing seats, and pads are securely reinstalled after replacement.
5. Conclusion
Bridge bearing maintenance is vital to ensuring structural safety and long-term durability. Regular inspection, cleaning, lubrication, and timely replacement prevent failures caused by material aging, corrosion, or uneven load transfer.
By following standardized inspection and replacement procedures, engineers can ensure that bridge bearings perform as designed, minimizing risk and maximizing bridge lifespan.