The Significance of Bridge Coating
Bridge coatings serve multiple critical purposes. They act as a protective shield against corrosion, which is a major threat to bridge structures, especially those made of steel. Corrosion can weaken the structural components of a bridge over time, leading to potential safety hazards. Coatings also enhance the aesthetic appeal of bridges, giving them a clean and well - maintained look. Additionally, they can improve the durability of the bridge surface, reducing the need for frequent and costly repairs.

Types of Bridge Coatings
There are several types of coatings used in bridge construction and maintenance. Epoxy coatings are highly popular due to their excellent adhesion and chemical resistance properties. They form a strong bond with the bridge surface, protecting it from harsh environmental factors such as moisture, salt, and chemicals. Polyurethane coatings are another common choice, known for their high abrasion resistance and flexibility. They can withstand the wear and tear caused by traffic and temperature variations. Fluoropolymer coatings offer exceptional weatherability and UV resistance, making them ideal for bridges located in areas with intense sunlight or extreme weather conditions.
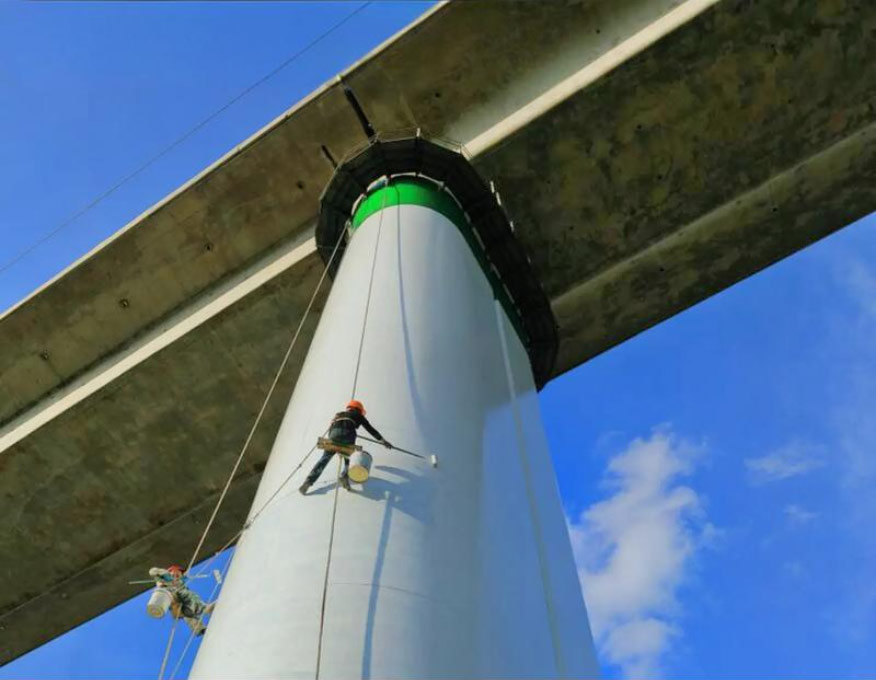

Bridge Coating Inspection Process
Visual Inspection
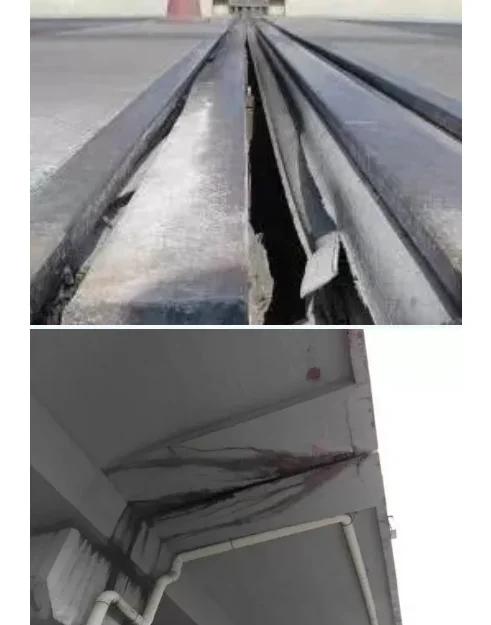
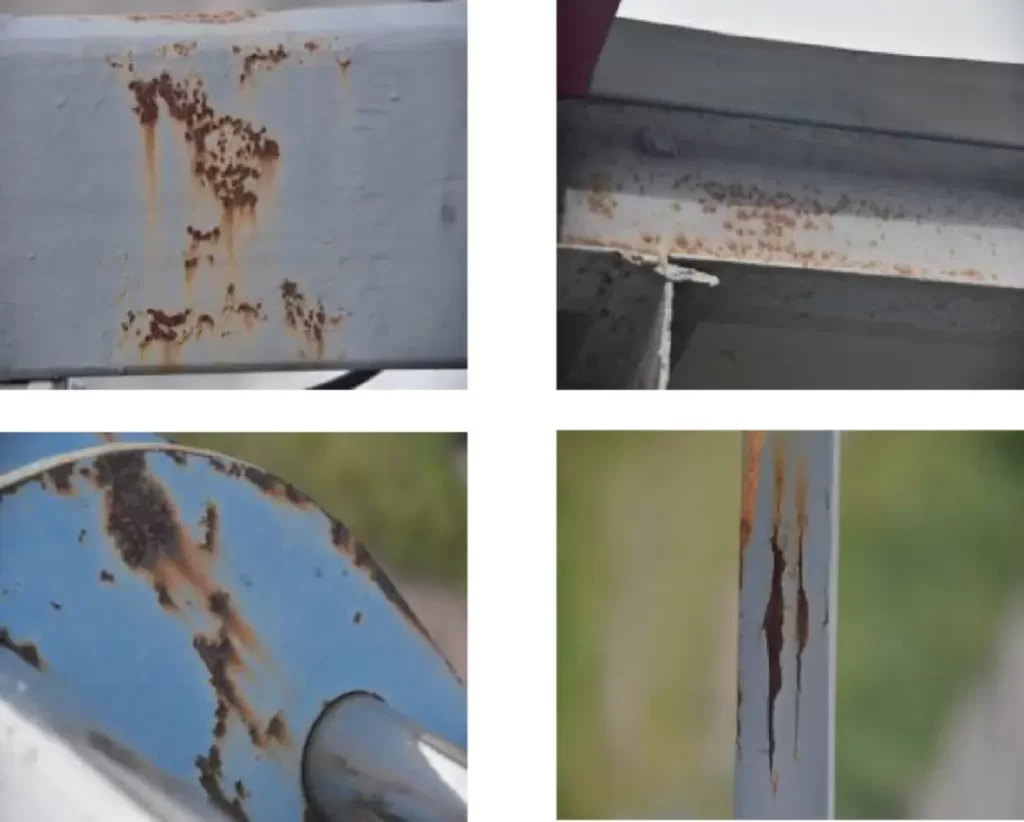
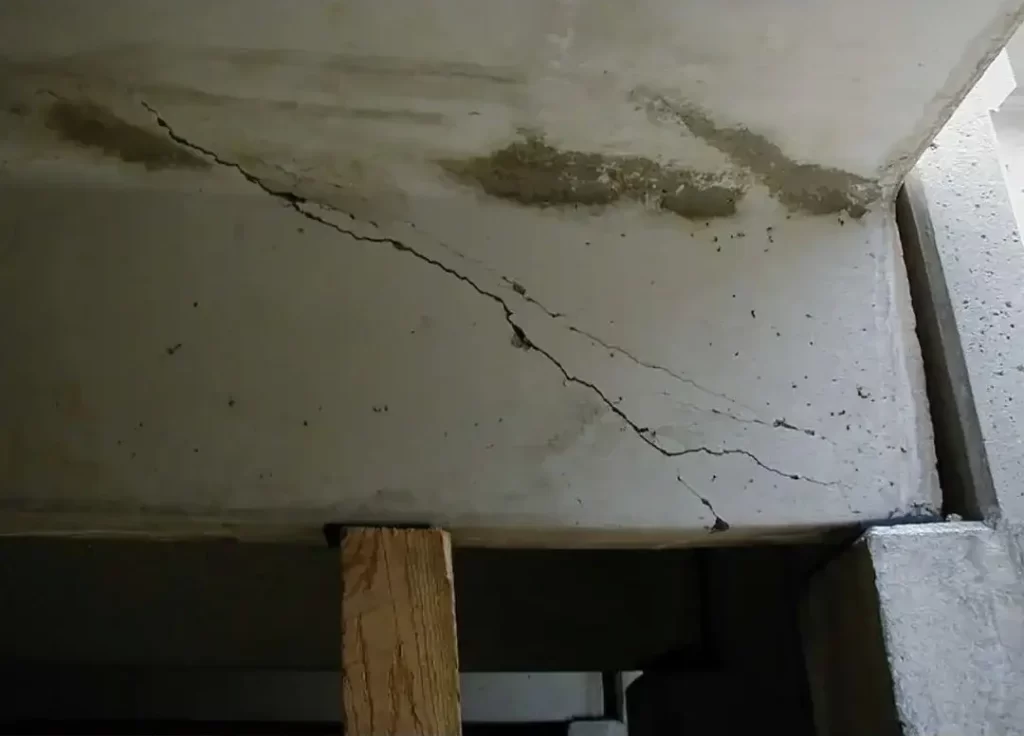
The first step in bridge coating inspection is a thorough visual inspection. Inspectors carefully examine the entire bridge surface, looking for signs of coating degradation such as cracking, peeling, blistering, or discoloration. Cracks in the coating can allow moisture to penetrate, accelerating the corrosion process. Peeling or blistering coatings indicate poor adhesion or underlying damage. Discoloration may be a sign of UV damage or chemical exposure.
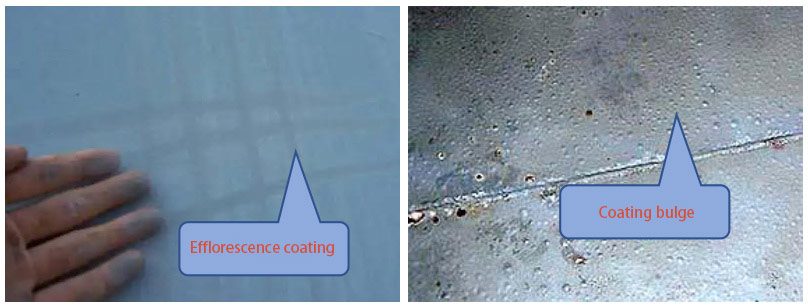
Thickness Measurement
Measuring the thickness of the coating is an essential part of the inspection process. The thickness of the coating affects its protective capabilities. Inspectors use specialized tools such as magnetic thickness gauges for steel bridges and non - magnetic gauges for other materials. The thickness of the coating should be within the specified range as per the manufacturer's recommendations and industry standards. If the coating is too thin, it may not provide adequate protection, while a coating that is too thick can lead to issues such as cracking or poor adhesion.
Adhesion Testing
Adhesion testing determines how well the coating is bonded to the bridge surface. A strong bond is necessary for the coating to effectively protect the bridge. There are different methods for adhesion testing, such as the pull - off test and the cross - hatch test. In the pull - off test, a small area of the coating is pulled with a calibrated device, and the force required to detach the coating is measured. In the cross - hatch test, a pattern of cuts is made in the coating, and a tape is applied and then removed to check for coating adhesion.
Integrating Advanced Drone Inspection for Coating Assessment
In addition to traditional visual and manual measurement techniques, modern drone-based bridge inspection technology has become an increasingly valuable tool for coating assessment. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and photogrammetric sensors can quickly capture detailed imagery of bridge surfaces — including hard-to-reach spots such as high girders, undersides of steel members, and areas above water — without the need for costly traffic closures or scaffolding.
With Riebo’s Drone Bridge Inspection Solution, aerial data collection is seamlessly combined with AI-powered defect recognition, enabling automated identification of coating degradation such as blistering, peeling, and surface corrosion. The result is a faster, more complete, and safer inspection workflow that enhances traditional coating inspection methods and feeds high-quality data into maintenance planning systems.

Environmental Considerations
Bridges are exposed to a wide range of environmental conditions, which can significantly impact the performance of the coating. In coastal areas, bridges are constantly exposed to salt - laden air, which can accelerate corrosion. Bridges in industrial areas may be exposed to chemicals and pollutants. Temperature variations and humidity levels also play a role in coating degradation. Inspectors need to take these environmental factors into account during the inspection process and recommend appropriate maintenance or coating replacement based on the severity of the environmental exposure.
The Role of Inspection in Maintenance and Repair
Regular bridge coating inspections help in early detection of coating problems. By identifying issues at an early stage, bridge owners can take proactive measures to address them. Minor coating defects such as small cracks or areas of low adhesion can be repaired relatively easily, preventing them from escalating into more serious problems. If the inspection reveals significant coating degradation, a decision can be made regarding whether to recoat the bridge or perform more extensive repairs. This not only helps in maintaining the structural integrity of the bridge but also in optimizing maintenance costs.
Conclusion
Bridge coating inspection is an integral part of bridge maintenance and safety management. By conducting regular inspections, bridge owners can ensure that their bridges are protected from corrosion and other forms of damage, extending their lifespan and ensuring the safety of the traveling public. With the right inspection techniques, proper understanding of coating types, and attention to environmental factors, bridges can continue to serve as reliable transportation links for many years to come.