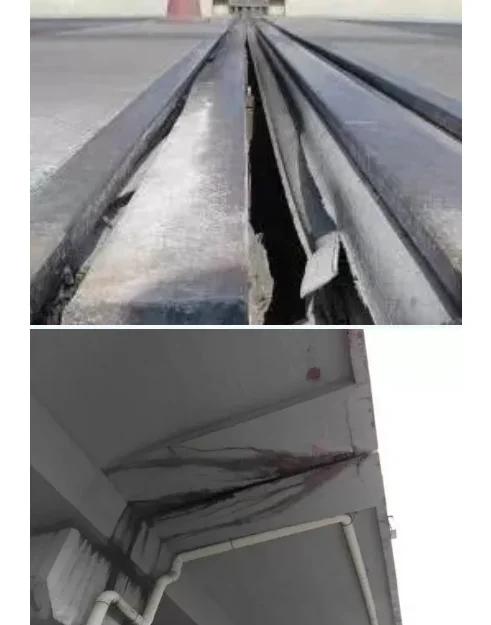
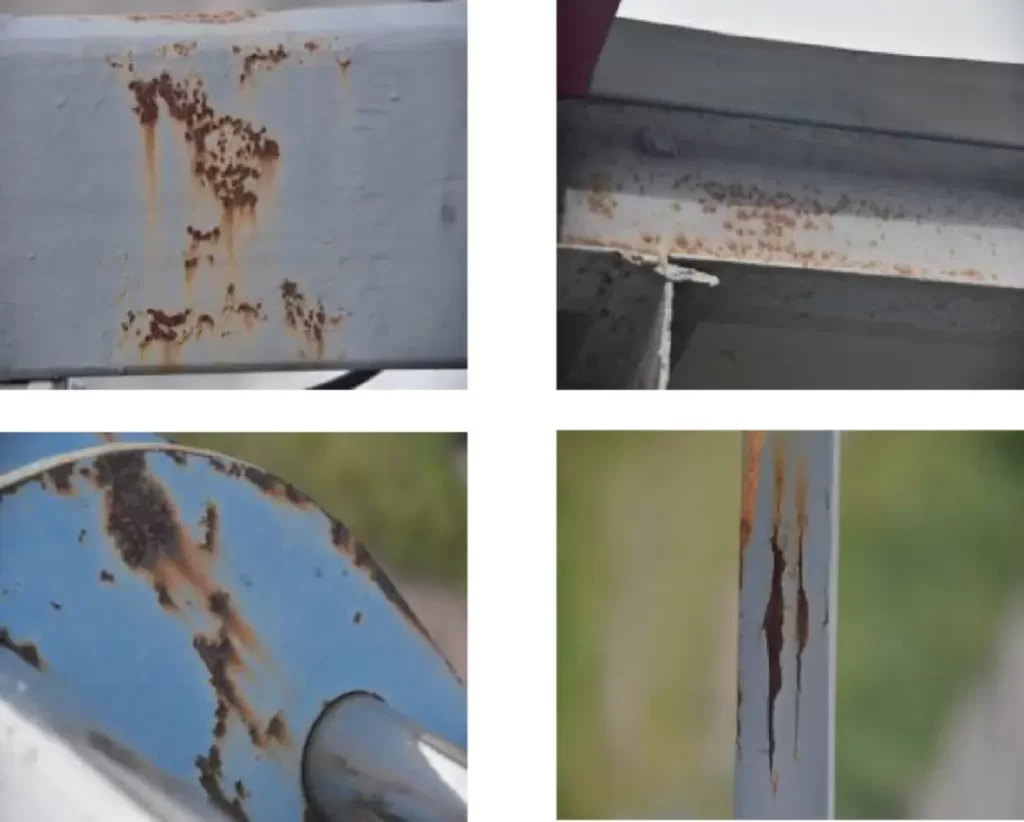
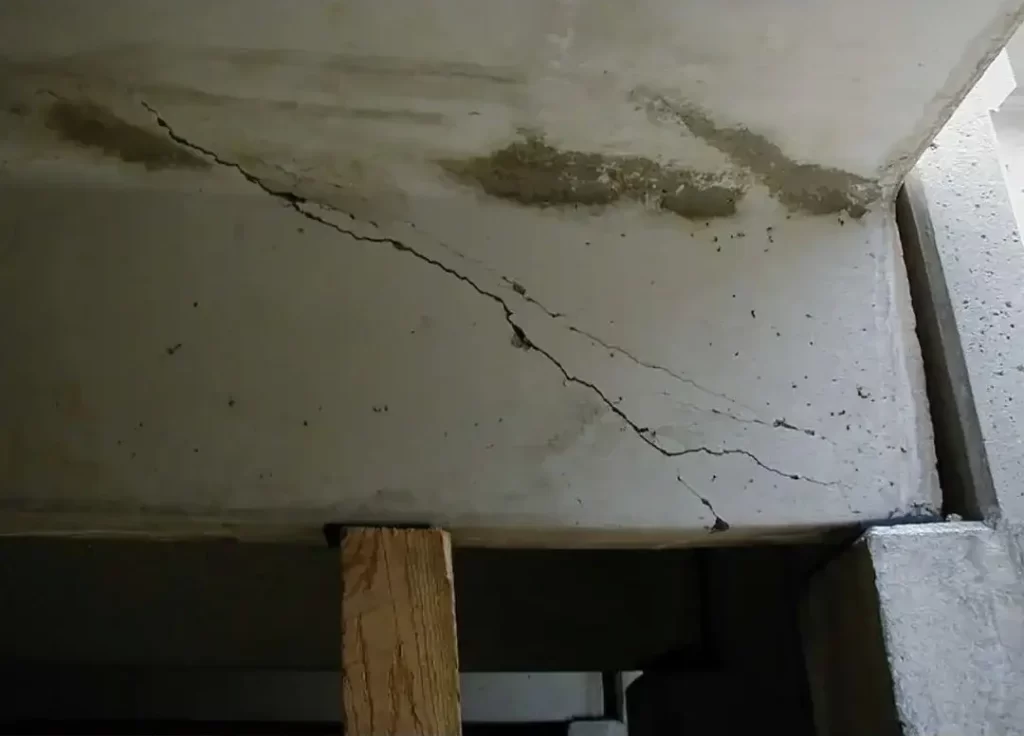
Bridge cable inspection is vital for ensuring the safety and durability of cable-stayed bridges. Stay cables — typically composed of polyethylene-sheathed parallel steel wires — endure UV exposure, moisture, and cyclic vehicle loads. Over years of service, these factors can cause sheath cracking, corrosion, wire breaks, and anchorage damage, all of which directly threaten structural stability.

Modern bridge maintenance now moves beyond manual checks to UAV-based and intelligent inspection methods that deliver precise, visual, and data-driven results.
Common Cable Defects and Inspection Importance
- Protective-layer damage: Aging or cracked PE sheaths lose their corrosion-protection capability.
- Steel-wire corrosion or breakage: Once exposed, wires rust and weaken load capacity.
- Anchorage-zone deterioration: Failed waterproof seals cause corrosion at anchorage pipes and fittings.
- Cable-force deviation: Uneven or reduced tension introduces abnormal stresses to the tower and deck.
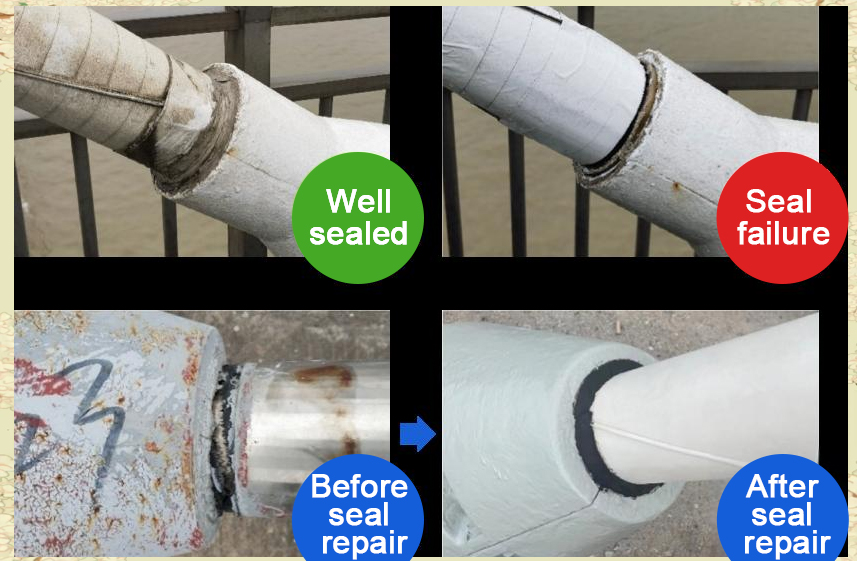
Timely detection of these problems prevents further deterioration and high repair costs. A scientific inspection program helps identify defects early, plan targeted maintenance, and extend bridge life cycles.
Core Bridge Cable Inspection Procedures
A comprehensive cable inspection normally includes five technical stages:
- Visual inspection of cable surface – Identify cracks, scratches, or sheath ruptures.
- Anchorage inspection – Evaluate waterproof seals and anti-corrosion conditions, especially in the lower anchorage.
- Non-destructive corrosion testing – Magnetostrictive guided-wave methods locate internal corrosion without removing the sheath.
- Window inspection – Local sheath removal for visual confirmation of wire corrosion or breaks.
- Cable-force measurement – Frequency and lift-off tests determine tension distribution and long-term stability.
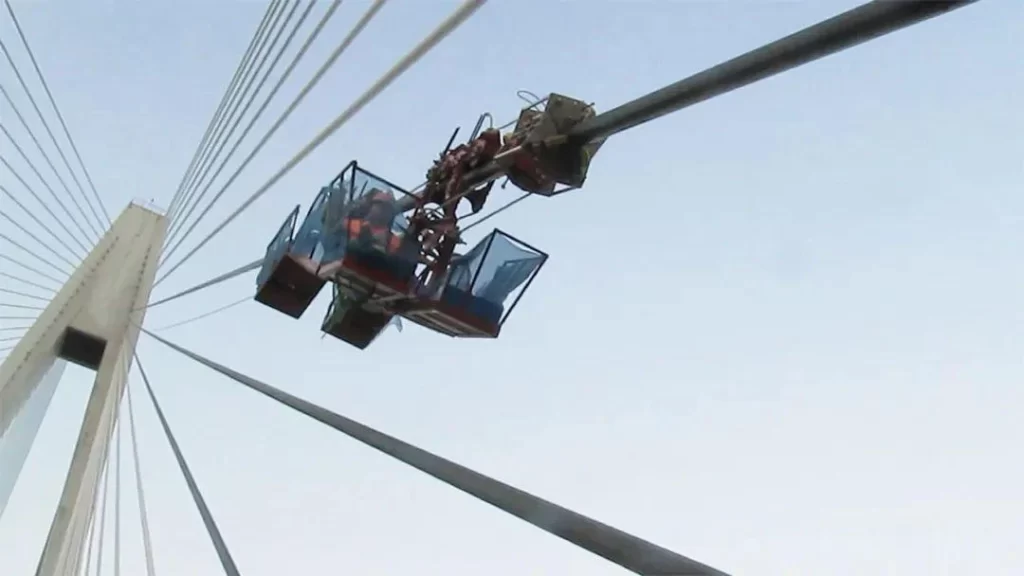

Traditional manual operations require scaffolding or rope access, which are slow, risky, and expensive — particularly for large-span cable-stayed bridges where many cables are hard to reach.
UAV Bridge Cable Inspection: Efficiency and Accuracy Redefined
High-Efficiency, Full-Coverage Detection
UAVs equipped with high-resolution zoom or infrared cameras can navigate between towers and decks, inspecting every cable segment — even hidden anchorage areas — within hours.
Compared to days or weeks of manual work, efficiency improves by 3–5 times while maintaining complete coverage.
Clear Visual Data and Geo-Tagged Defect Records
Through multi-angle hovering and close-range imaging, drones capture tiny cracks, rust marks, or seal failures. Each image is GPS-tagged to build a traceable digital inspection archive, enabling long-term monitoring and trend analysis.
Enhanced Safety and Cost Savings
No scaffolds, no high-altitude operations — UAV inspections remove most human-safety risks. Lower labor and equipment costs make this approach especially beneficial for aging or complex bridge structures.
Targeted Deep Inspection Support
UAVs act as the first-stage filter in a multi-step inspection chain. They pinpoint roughly 10–15 % of cables showing visible anomalies, allowing engineers to focus advanced NDT or force testing on these critical areas — reducing unnecessary workload and optimizing resources.
Limitations and Hybrid Inspection Strategy
While UAVs excel in visual assessment, they cannot see through cable sheaths or measure tension directly. Hidden corrosion, broken wires, or internal water accumulation still require guided-wave or lift-off testing.
Moreover, adverse weather (strong wind, heavy rain, dense fog) affects flight stability and image quality.
To achieve the best results, engineers adopt a hybrid model: “UAV preliminary screening + specialized in-depth inspection.” This layered workflow ensures both speed and precision, aligning with the principle of “from surface to core, step by step.”
Intelligent Bridge Cable Inspection
The integration of AI image recognition, digital-twin modeling, and big-data analytics is transforming bridge cable inspection into a smart, predictive maintenance system. Automated defect identification, cable-force trend prediction, and maintenance scheduling are becoming achievable in real time, enabling safer and more sustainable bridge management.
Conclusion
Bridge cable inspection safeguards the long-term performance of cable-stayed bridges. UAV-based inspection has proven to be a reliable, cost-effective, and safe alternative to traditional manual methods.
By combining aerial visual data with guided-wave testing and intelligent analytics, engineers can build a complete, data-driven maintenance strategy that extends structural service life and enhances public safety.