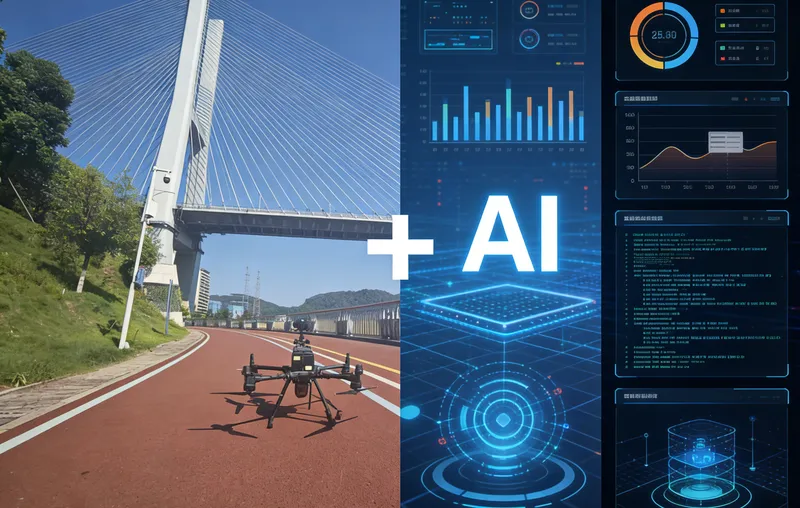
With the continuous advancement of aerial photography and remote sensing technologies, drone applications began expanding rapidly across various industries. Among the different types of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), multi-rotor drones became widely used due to their simple structure, affordable cost, and flexibility.
Even before the introduction of artificial intelligence into bridge inspection, drones had already started playing an important role in high-efficiency, low-cost bridge surveys and infrastructure assessments.

Ensuring Bridge Safety through Regular Inspections
Bridge inspections are essential to ensure structural safety and long-term reliability. They help detect defects and abnormal conditions early, providing a scientific basis for timely maintenance and reinforcement.
Regular inspections can:
- Extend bridge service life,
- Enhance load-bearing capacity,
- Reduce repair costs or avoid full reconstruction,
- Provide technical data for bridge design improvements and engineering standards.
1. Limitations of Traditional Inspection Methods
Traditionally, bridge maintenance departments conducted periodic inspections using manual visual observation or simple auxiliary tools such as bridge inspection vehicles and telescopes.
Inspectors mainly checked for:
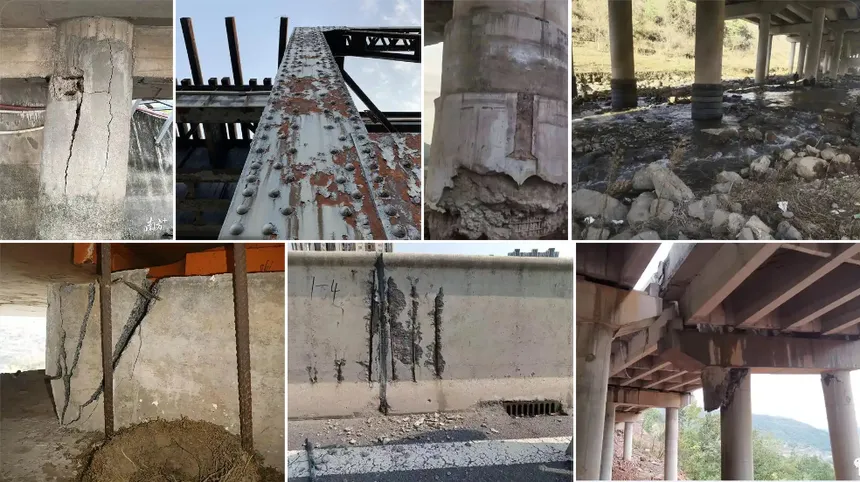
- Cracks or spalling in the main components,
- Exposed or corroded rebar, and bearing dislocation or voids.

However, these conventional methods had major limitations—especially for special structures like cable-stayed bridges, suspension bridges, and steel-tube arch bridges, as well as large-span or high-pier bridges. Components such as deck undersides, pylons, cables, and lightning rods were often beyond reach.
Manual inspection of these areas was:
- Time-consuming,
- Dangerous, and Often resulted in inspection blind spots, leaving hidden structural risks undetected.
2. Advantages of Drone-Based Bridge Inspection
Compared to conventional inspection methods, drones brought several key advantages:
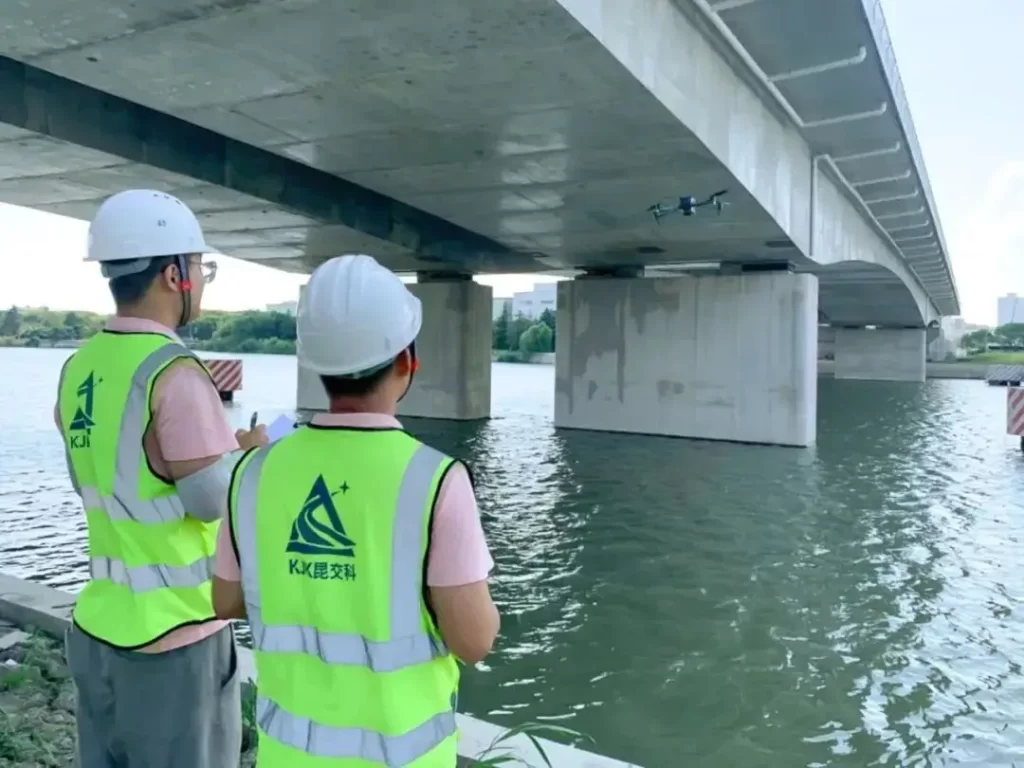

(1) Low Operating Cost
Drone-based inspection relied on mature technologies such as GNSS navigation, digital imaging, and wireless control. All equipment was battery-powered, requiring no scaffolding or heavy vehicles, making operational costs far lower than traditional bridge inspection cars or manual methods.
(2) High Precision
Multi-rotor drones equipped with high-resolution cameras could capture fine details of bridge defects. Operators could adjust shooting angles flexibly and perform repeated measurements to ensure data accuracy.
(3) Flexibility and Wide Applicability
Only basic field equipment—a laptop, controller, and off-road vehicle—was needed for inspection.
Drones required no dedicated takeoff or landing zones, making them ideal for routine bridge inspections in both urban and rural environments.
(4) Easy Maintenance and Upgrade
Drone systems were modular in design, with external payloads that could be easily replaced or upgraded to meet different inspection needs.
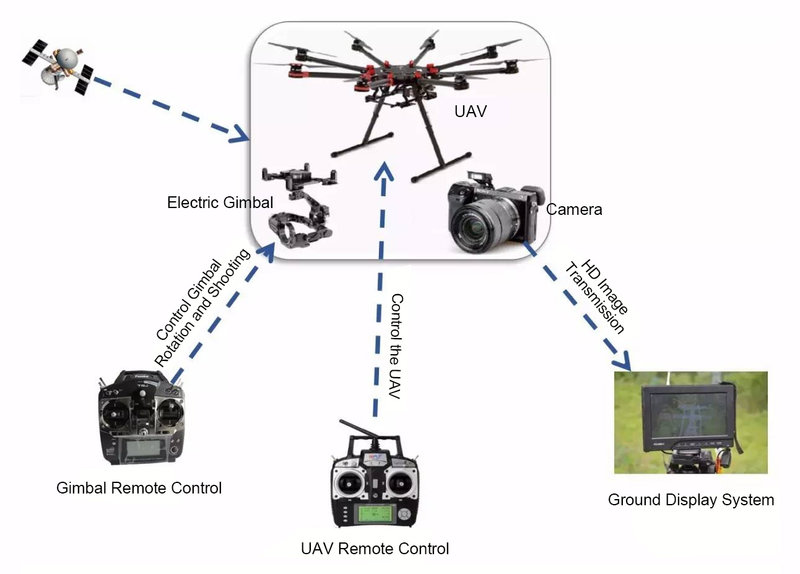
3. Components of a Drone-Based Bridge Inspection System
A typical drone bridge inspection system consisted of:
- The drone platform,
- Data transmission system,
- Payload system (camera and sensors),
- Ground control station, and other supporting equipment.
These components worked together to collect, transmit, and store inspection data for later analysis.
 4. Main Inspection Tasks
4. Main Inspection Tasks
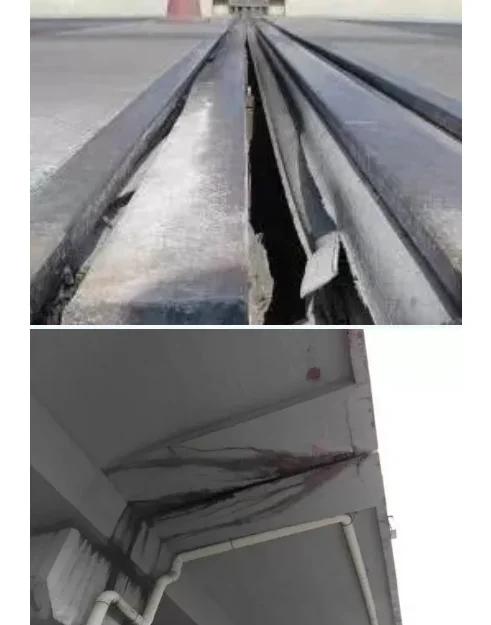
(1) Concrete Surface Defects
Inspection of honeycombing, exposed rebar, spalling, delamination, and cracks on bridge decks and piers.

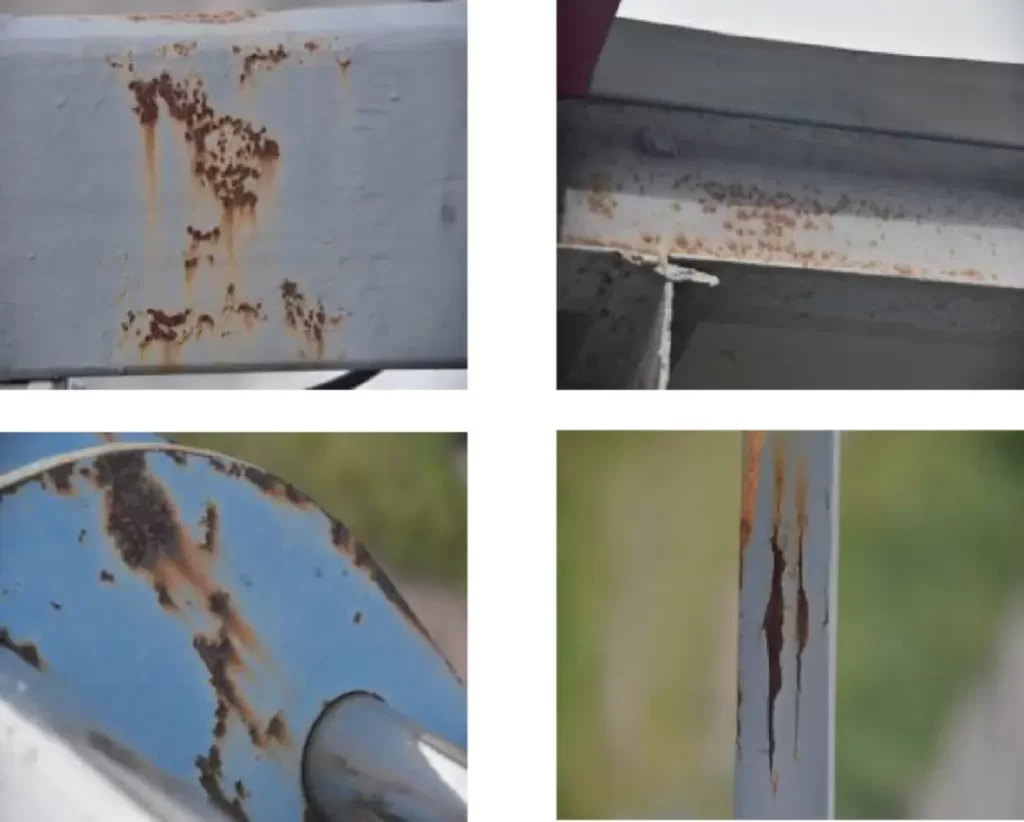
(2) Steel Structure Components
Detection of missing or loose high-strength bolts on steel bridge elements.

(3) Other Structural Defects
Detection of bearing displacement, deck pavement damage, and other issues affecting structural stability.
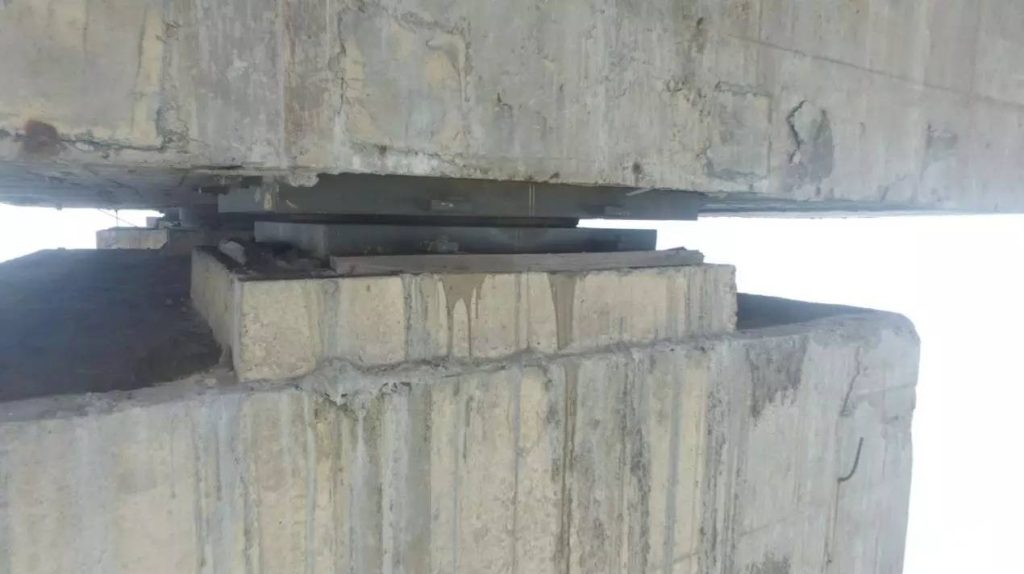

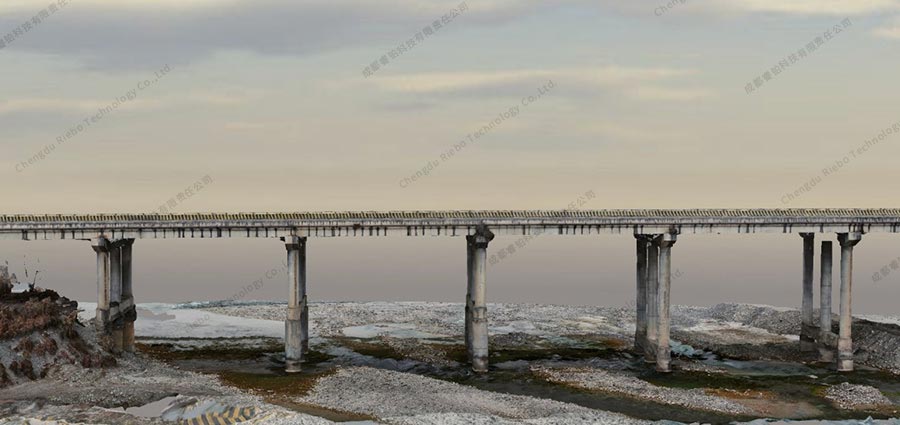
(4) 3D Bridge Modeling
By capturing bridge structures from multiple angles, drone images were processed through specialized software to create high-precision 3D bridge models. These digital models were archived as part of the bridge’s maintenance record, serving as a reference for future repair and structural analysis.

5. Operational Guidelines and Safety Precautions
- Team Setup – Drone inspection usually required two operators: one controlling the flight path and the other managing imaging and data collection. Before takeoff, all systems were tested, and flight commands were coordinated for safe operation.
- Flight Distance Control – Typical inspection distances were:
- About 5 meters from bridge piers or towers,
- Around 10 meters for cables or complex steel components,
adjusted based on the structure and environmental conditions.
- Real-Time Monitoring – Drone position and video feed were displayed on the ground control station.
When potential defects were detected, the operator could hover the drone to capture high-definition close-up images for further analysis.
Data was stored onboard to avoid wireless transmission loss during long-distance flights. - Environmental Considerations – Flight quality was affected by sunlight, wind, and weather conditions.
Inspections were best conducted on clear, calm days with optimal lighting to ensure high-quality imaging and reduce operational risks. - Post-Processing and Analysis – After fieldwork, images and videos were downloaded and analyzed using visual processing software to identify defect types and dimensions. The assessment followed national standards such as the Highway Technical Condition Evaluation Standard, ensuring consistent and accurate results.
Before AI: The Foundation of Intelligent Bridge Inspection
These pre-AI drone inspection practices laid the technical foundation for today’s intelligent bridge inspection systems.
Although the analysis still depended on manual image interpretation, drones already made it possible to inspect hard-to-reach areas safely and efficiently, greatly improving bridge maintenance workflows.
Integration with Riebo’s Drone Bridge Inspection Solution
Building on this foundation, Riebo’s Drone Bridge Inspection Solution takes drone-based bridge inspection to the next level. By combining advanced AI defect recognition, high-resolution imaging, and automated data analysis, Riebo transforms drone inspection from manual observation into smart, data-driven diagnostics.

This integration enables faster, safer, and more accurate inspections—turning traditional drone surveys into a complete intelligent bridge health monitoring system that supports long-term safety and operational efficiency.