1. Project Background
As oblique photogrammetry technology continuously advances, it has been widely adopted in applications such as cadastral surveying, terrain mapping, smart cities, and architectural analysis. In this project, the client engaged Riebo technology to carry out drone-based oblique photogrammetry over a typical urban area to generate the foundational 3D data required for building sunlight and shading analysis.
2. Client
Lianyungang Survey & Mapping Institute Co., Ltd. is a Grade A certified surveying and mapping organization based in Jiangsu Province, China. The company has extensive experience in GPS control surveying, large-scale orthophoto production, and topographic mapping at large scales (1:500 and 1:1000). It has also executed major cadastral and urban mapping programs and provided long-term spatial data support for regional planning and infrastructure development.
3. Survey Area
The project area is located in Ganyu District of Lianyungang City, Jiangsu Province, China. The region exhibits a warm temperate monsoon climate with abundant sunlight, making it suitable for aerial surveying operations. Most buildings in the survey area are high-rise structures, with heights reaching up to approximately 75 m. Fieldwork was conducted in optimal sunlight conditions between 10:00 and 12:00 with mild winds, ensuring good image quality.
4. Equipment Used
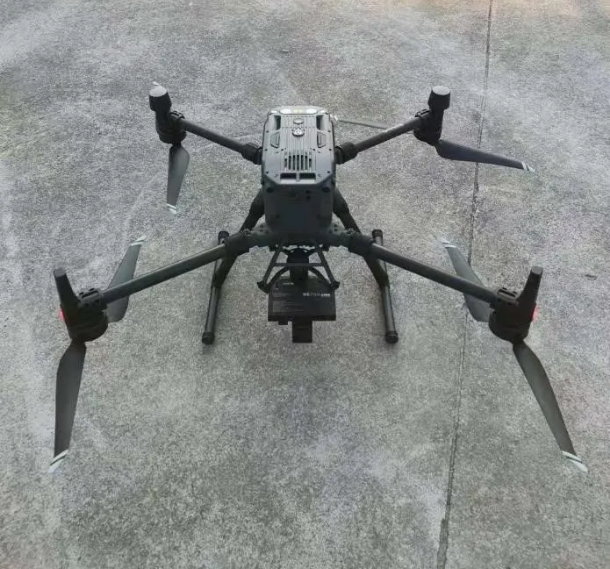
- Drone Platform: DJI M300 RTK UAV — offers up to 55 minutes flight endurance, strong wind resistance, precise RTK positioning, and robust autonomous flight capabilities.
- Camera: Riebo D2 Oblique Photogrammetry Camera — lightweight (~800 g with gimbal), suitable for multi-rotor mounting. It provides high-resolution oblique imaging while maximizing operational efficiency and ROI for localized high-resolution 3D data capture tasks.
5. Flight Mission Details
Ground Control:
Six ground check points and twelve building corner checkpoints were established and surveyed using RTK equipment to provide accurate ground references for later model accuracy assessment.
Flight Planning:
Due to the presence of tall buildings, two separate flight passes were conducted:
- First pass: Flight altitude ~107 m, resulting in 1.8 cm GSD.
- Second pass: Flight altitude ~150 m, resulting in 2.5 cm GSD, ensuring complete coverage of building tops and complex structures.
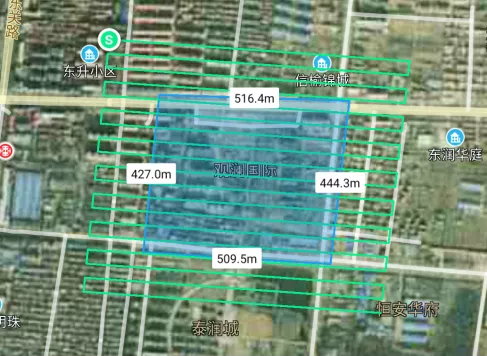
Survey Coverage:
Although the effective area was ~0.2 km², planning with expanded flight margins resulted in ~0.44 km² of actual flown area. Overlapping was set at ~80% forward and ~70% side overlap to ensure dense imagery for high-quality 3D reconstruction. A total of 13,465 aerial images were captured with uniform color balance and clarity, meeting production requirements.
6. Data Processing Workflow
Image Preprocessing:
Collected aerial images were processed using Skyscanner software, which filters and removes invalid photos before exporting data to photogrammetry processing software. This significantly improves photogrammetric computation efficiency.
Aerial Triangulation & Model Production:
High-performance computer clusters (Intel® Core™ i9, 128 GB RAM) were used.
After filtering, 8,135 valid images remained for processing. Using ContextCapture software, the aerial triangulation and model building process took approximately 12 hours total.
Accuracy Validation:
Using EPS software, model precision was tested against the measured check points. Both horizontal and vertical errors were less than 2 cm, meeting the national standard accuracy requirement for 1:500 topographic survey.
DLG Production:
Digital Line Graphic (DLG) data were generated in CASS3D — only building footprint vectors were required for the ensuing sunlight/shading analysis.

7. Project Results
Model Quality:
The photogrammetric 3D model exhibited high geometric fidelity and texture continuity across building façades and rooftops, providing accurate base data for solar analysis.

Sunlight Analysis:
Using the generated building 3D model, sunlight and shading analysis was successfully completed, offering actionable spatial insight for architectural evaluations.
8. Conclusions & Future Application
Validation results confirmed that data captured by the DJI M300 RTK with Riebo D2 Oblique Camera met national survey precision standards. Compared with traditional ground-based measurement techniques, oblique photogrammetry enabled the capture of multi-angular imagery, facilitating detailed 3D reconstruction with significant time and resource savings.
The successful application of oblique photogrammetry for sunlight analysis highlights its value in architecture, urban planning, construction verification, and cut/fill surveys — demonstrating adaptability across diverse surveying tasks.